- Tel: 858.663.9055
 Email: info@nsjbio.com
Email: info@nsjbio.com
- Tel: 858.663.9055
- Email: info@nsjbio.com
Apoptosis Marker Antibodies are indispensable reagents for studying programmed cell death, a tightly regulated process essential for maintaining tissue balance and organismal health. Unlike necrosis, which is uncontrolled and inflammatory, apoptosis follows a precise cascade of signaling events that dismantle a cell in an orderly fashion. This process allows the body to remove damaged, infected, or unnecessary cells without triggering widespread inflammation.
Molecular hallmarks of apoptosis include activation of caspases, release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, cleavage of structural and nuclear proteins such as PARP, and externalization of phosphatidylserine on the plasma membrane. Collectively, these steps ensure that cells are dismantled efficiently and that their remnants are cleared by phagocytes. Dysregulation of apoptosis has profound consequences: failure to undergo apoptosis contributes to cancer and autoimmunity, while excessive apoptosis leads to neurodegeneration and ischemic injury.
By targeting caspase family proteins, BCL-2 regulators, death receptors such as Fas, mitochondrial markers like cytochrome c, and cell-surface indicators such as Annexin V, Apoptosis Marker Antibodies allow researchers to interrogate every stage of the death cascade. These tools are central to oncology, neuroscience, immunology, toxicology, and therapeutic discovery.
NSJ Bioreagents provides a comprehensive collection of Apoptosis Marker Antibodies, validated for immunohistochemistry (IHC), western blot (WB), immunofluorescence (IF), flow cytometry (FACS), and ELISA. Each antibody undergoes stringent quality control for specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility across platforms.
Researchers choosing Apoptosis Marker Antibodies from NSJ Bioreagents benefit from:
Validated Performance: Each antibody is tested in multiple applications and against positive and negative controls.
Reproducibility: Guaranteed batch-to-batch consistency ensures reliable long-term use.
Assay Versatility: Compatible with tissue staining, lysate analysis, and quantitative assays.
Detailed Datasheets: Each product includes technical information, suggested controls, and protocol tips.
Translational Relevance: Many antibodies are validated in both model systems and human samples, making them suitable for research and clinical workflows.
This combination of specificity, reproducibility, and support ensures that Apoptosis Marker Antibodies are not just laboratory reagents but critical components of translational pipelines.
The Apoptosis Marker Antibodies portfolio supports a broad range of applications that extend across cell biology, pathology, and therapeutic discovery.
Detect altered expression of BAX, BCL-2, caspase-3, and cleaved PARP in tumor samples.
Support research into resistance to chemotherapy and radiation, where cells evade apoptosis.
Validate biomarkers for predicting patient response to targeted therapies such as BCL-2 inhibitors.
Enable mechanistic studies of how oncogenes and tumor suppressors regulate apoptosis.
Provide translational tools for biomarker-driven oncology pipelines.
Detect apoptotic neuronal loss in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and ALS models.
Clarify how mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress trigger caspase-dependent pathways.
Validate apoptosis biomarkers for cognitive decline and memory impairment.
Support therapeutic discovery of neuroprotective agents that block inappropriate apoptosis.
Provide translational insights into how apoptosis contributes to synaptic pruning and glial activation.
Detect Fas/FasL-mediated apoptosis in T-cell regulation and cytotoxic killing.
Support studies of immune tolerance, including deletion of autoreactive lymphocytes.
Clarify how defective apoptosis contributes to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis.
Provide biomarkers for studying immune checkpoint pathways.
Support translational research into therapies that restore balance to apoptotic signaling in immune cells.
Detect apoptosis during tissue remodeling in embryogenesis.
Clarify programmed cell death in shaping the nervous system, digits, and immune repertoire.
Provide markers for studying stem cell differentiation, survival, and self-renewal.
Support comparative developmental biology studies across vertebrate models.
Extend into regenerative medicine, where controlled apoptosis influences tissue repair.
Detect apoptosis triggered by drugs, toxins, and environmental stressors.
Provide tools for pharmaceutical safety screens, identifying compounds that induce unwanted cell death.
Support high-throughput assays for apoptosis in hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity.
Validate apoptosis biomarkers for regulatory toxicology studies.
Extend into translational pharmacology, where apoptosis markers guide dose selection.
Provide diagnostic markers for evaluating apoptosis dysregulation in cancer biopsies.
Enable patient stratification based on apoptosis pathway alterations.
Support clinical trials measuring apoptosis biomarkers as indicators of therapeutic efficacy.
Contribute to personalized medicine approaches by linking apoptosis profiles to treatment outcomes.
Ensure reproducibility and reliability from basic biology to clinical applications.
Apoptosis is one of the most conserved and critical biological processes, influencing virtually every aspect of health and disease. Apoptosis Marker Antibodies allow scientists to study this process at multiple levels: initiation, signaling cascades, execution, and clearance.
In oncology, they reveal how tumors evade apoptosis by overexpressing anti-apoptotic proteins such as BCL-2 or downregulating pro-apoptotic molecules like BAX. In neurobiology, they clarify how excessive or misdirected apoptosis leads to neuronal death and progressive cognitive decline. In immunology, they define the role of apoptosis in immune tolerance and cytotoxic T-cell function. In toxicology, they help detect early biomarkers of tissue injury.
Clinically, apoptosis markers are increasingly used for diagnostics and treatment monitoring. For example, detection of cleaved caspase-3 or Annexin V binding is employed in evaluating treatment response in oncology trials. Reliable Apoptosis Marker Antibodies ensure that these biomarkers can be detected consistently, bridging laboratory discovery with clinical relevance.
Apoptosis balances survival and death at the cellular level, and its disruption drives many of the world’s most pressing diseases. Apoptosis Marker Antibodies provide validated reagents to study caspases, BCL-2 proteins, mitochondrial mediators, and death receptors across oncology, neuroscience, immunology, and translational research. By ensuring specificity, reproducibility, and assay versatility, these antibodies remain indispensable for advancing apoptosis research and improving clinical outcomes.
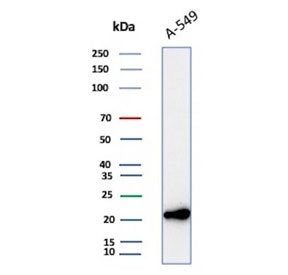
Western blot testing of human A549 cell lysate with Bax antibody (clone 2D2). Predicted molecular weight ~21 kDa.
|
| ||

|