- Tel: 858.663.9055
 Email: info@nsjbio.com
Email: info@nsjbio.com
- Tel: 858.663.9055
- Email: info@nsjbio.com
Ig Antibody reagents target immunoglobulins, the Y-shaped proteins central to adaptive immunity. Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are secreted by plasma cells in response to antigens. They circulate through blood and tissues, neutralizing pathogens, activating complement, and guiding immune effector functions.
The immunoglobulin family is divided into five major classes—IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE—each with unique structural and functional roles. IgG provides long-term protection and is the most abundant in serum; IgA protects mucosal surfaces; IgM acts as the first responder in infection; IgE mediates allergy and defense against parasites; IgD functions in B cell activation. The Ig Antibody provides precise detection of these molecules, while Immunoglobulin Antibodies more broadly enable study of antibody class switching, immune memory, and dysregulation in disease.
Because antibodies are both biomarkers and therapeutic agents, reagents targeting immunoglobulins are indispensable in immunology, pathology, and clinical research.
NSJ Bioreagents provides Ig Antibodies validated for immunohistochemistry, western blotting, ELISA, flow cytometry, and immunofluorescence. Each Ig Antibody undergoes stringent quality control to ensure specificity for the intended isotype or subclass, minimizing cross-reactivity.
By selecting an Ig Antibody from NSJ Bioreagents, scientists gain reagents optimized for reproducibility and accuracy. Our Immunoglobulin Antibodies deliver clear results across assays, whether the goal is monitoring antibody production, diagnosing disease, or validating biomarkers. Detailed datasheets, recommended controls, and optimized protocols ensure researchers can confidently apply these reagents in both discovery and translational settings.
The Ig Antibody is a versatile tool with broad applications in immunology and medicine.
Ig Antibodies measure serum levels of IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE.
The Ig Antibody clarifies immune response to infection and vaccination.
Immunoglobulin Antibodies support studies of immune memory and antibody persistence.
Ig Antibodies detect IgE in allergic disease.
The Ig Antibody is applied in asthma, rhinitis, and food allergy research.
Immunoglobulin Antibodies support biomarker validation in hypersensitivity.
Ig Antibodies identify autoantibodies associated with lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
The Ig Antibody helps clarify pathogenic versus protective antibody responses.
Immunoglobulin Antibodies support diagnostics and disease stratification.
Ig Antibodies measure antibody titers following viral and bacterial infection.
The Ig Antibody validates immune protection after vaccination.
Immunoglobulin Antibodies support serological testing and surveillance studies.
Ig Antibodies are used in lymphoma and myeloma research to study abnormal immunoglobulin expression.
The Ig Antibody supports characterization of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies.
Immunoglobulin Antibodies contribute to biomarker discovery in immune-oncology.
Ig Antibodies clarify B cell maturation and class-switch recombination.
The Ig Antibody highlights plasma cell differentiation and antibody secretion.
Immunoglobulin Antibodies support studies of germinal center biology.
Ig Antibodies are applied in drug development, vaccine trials, and diagnostics.
The Ig Antibody supports patient stratification in immunotherapy studies.
Immunoglobulin Antibodies are essential in monitoring therapeutic efficacy.
Immunoglobulins represent the adaptive immune system’s most powerful weapon against infection and disease. The Ig Antibody provides a reliable means to detect and quantify these proteins, while Immunoglobulin Antibodies more broadly support discovery, diagnostics, and translational medicine.
In basic science, Ig Antibodies illuminate antibody diversity and immune function. In clinical research, the Ig Antibody enables serological testing, allergy diagnostics, and biomarker validation. In oncology, Immunoglobulin Antibodies clarify immune dysregulation in hematological malignancies and support therapeutic development.
Clinically, immunoglobulins are measured to diagnose immune deficiencies, monitor autoimmune conditions, and evaluate vaccine responses. The Ig Antibody therefore bridges molecular immunology with clinical application, ensuring accuracy and reproducibility in research and medicine.
Immunoglobulins are central to adaptive immunity and clinical diagnostics. The Ig Antibody equips scientists and clinicians with a precise tool for detecting immunoglobulin proteins, while Immunoglobulin Antibodies more broadly support research in immunology, infectious disease, oncology, and translational science. By ensuring reliable detection, these reagents remain indispensable for advancing immune research and improving patient outcomes.
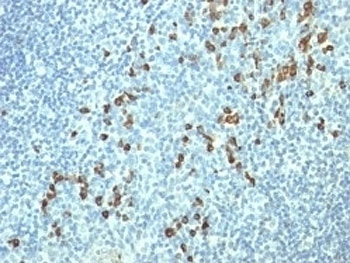
IHC staining of FFPE human tonsil tissue with Lambda Light Chain antibody (clone HP6054).