- Tel: 858.663.9055
 Email: info@nsjbio.com
Email: info@nsjbio.com
- Tel: 858.663.9055
- Email: info@nsjbio.com
Cytokeratin 8 Antibody reagents target keratin 8 (KRT8), a type II intermediate filament protein expressed in simple epithelial cells lining internal organs. KRT8 partners with keratin 18 to form heterodimers, providing cytoskeletal stability, mechanical resilience, and protection against stress-induced apoptosis. Cytokeratin 8 is broadly expressed in the liver, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, and other epithelial tissues, making it a fundamental epithelial marker.
Alterations in KRT8 expression are implicated in multiple diseases. Elevated levels occur in carcinomas of the liver, colon, breast, pancreas, and lung, while mutations have been linked to liver diseases such as cryptogenic cirrhosis. Because of this dual role in physiology and pathology, the Cytokeratin 8 Antibody is widely applied in cancer research, pathology, and cell biology. The CK8 Antibody also supports developmental biology, regenerative research, and translational medicine.
NSJ Bioreagents supplies Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies validated for immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, western blotting, ELISA, and flow cytometry. Each Cytokeratin 8 Antibody undergoes rigorous testing for specificity and reproducibility to ensure accurate detection in complex tissue environments.
By selecting Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies from NSJ Bioreagents, researchers gain access to reagents optimized for consistency and clarity. Our antibodies provide strong cytoplasmic staining in epithelial tissues, reproducible protein detection in lysates, and robust performance across diverse experimental platforms. Comprehensive datasheets, suggested controls, and validated protocols further support reliable outcomes.
The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody supports a wide range of applications across biology and clinical research.
Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies detect carcinomas in liver, colon, breast, and pancreas.
The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody highlights tumor progression and metastatic potential.
CK8 Antibody reagents validate biomarkers for prognosis and therapy response.
Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies confirm epithelial origin in tissue biopsies.
The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody is used in immunohistochemistry panels for carcinoma classification.
CK8 Antibody reagents distinguish epithelial malignancies from non-epithelial tumors.
Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies identify mutations linked to chronic liver disease.
The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody supports research into cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
CK8 Antibody reagents are applied in biomarker discovery for liver pathology.
Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies track epithelial differentiation in embryogenesis.
The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody validates lineage specification in organoid and stem cell models.
CK8 Antibody tools support regenerative medicine targeting epithelial tissues.
Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies highlight roles in apoptosis and cytoskeletal stability.
The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody supports studies of epithelial resilience under stress.
Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies are validated in biomarker-driven oncology trials.
The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody supports translational medicine by linking laboratory discovery to patient care.
CK8 Antibody reagents provide tools for evaluating epithelial biomarkers in precision medicine.
KRT8 is a fundamental cytoskeletal protein central to epithelial biology and disease. The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody equips researchers with precise tools for detecting and studying this protein, while the CK8 Antibody complements broader applications in pathology and translational research.
In oncology, Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies highlight tumor progression and help classify epithelial carcinomas. In liver disease research, the Cytokeratin 8 Antibody supports the study of genetic mutations and hepatocellular pathology. In stem cell biology, CK8 Antibody reagents ensure lineage fidelity in epithelial differentiation.
Clinically, Cytokeratin 8 is a widely used diagnostic marker. Accurate detection with Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies helps pathologists confirm carcinoma origin, guide treatment decisions, and evaluate prognosis. By ensuring reproducibility, the Cytokeratin 8 Antibody bridges discovery, diagnostics, and clinical medicine.
Cytokeratin 8 is a key intermediate filament protein in epithelial tissues and a valuable biomarker in cancer and liver disease. The Cytokeratin 8 Antibody equips researchers and clinicians with validated reagents for detecting KRT8 in oncology, hepatology, and developmental biology. Together, Cytokeratin 8 Antibodies and the CK8 Antibody remain indispensable tools for advancing epithelial research and improving diagnostic accuracy.
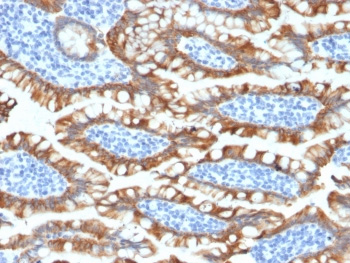
IHC testing of FFPE human small intestine tissue with recombinant Cytokeratin 8 antibody (clone KRT8/2174R, cat # V3562).