- Tel: 858.663.9055
 Email: info@nsjbio.com
Email: info@nsjbio.com
- Tel: 858.663.9055
- Email: info@nsjbio.com
KRT1 Antibody detects keratin 1, a type II intermediate filament protein expressed in the suprabasal layers of the epidermis. KRT1 pairs with keratin 10 to form heterodimers that provide structural reinforcement in differentiated keratinocytes. This keratin pair is crucial for maintaining the strength and resilience of the skin barrier, particularly in the upper spinous and granular layers of stratified epithelia.
Mutations in KRT1 are linked to epidermolytic ichthyosis and palmoplantar keratoderma, inherited skin disorders characterized by blistering, scaling, and hyperkeratosis. Abnormal expression of KRT1 has also been reported in inflammatory skin disease and squamous cell carcinoma. The KRT1 Antibody is therefore a key tool for studying epidermal differentiation, keratinopathies, and tumor biology.
Because of its restricted expression pattern and disease relevance, Keratin 1 Antibody reagents are widely applied across dermatology, oncology, and regenerative medicine.
NSJ Bioreagents provides KRT1 Antibodies validated for immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, western blotting, ELISA, and flow cytometry. Each KRT1 Antibody undergoes rigorous testing for specificity to keratin 1 and minimal cross-reactivity with related keratins such as KRT10 or KRT2.
By selecting a KRT1 Antibody from NSJ Bioreagents, researchers gain reagents optimized for reproducibility. Our antibodies provide strong staining in suprabasal epidermis, consistent protein detection in lysates, and dependable performance across multiple applications. With comprehensive datasheets, recommended controls, and validated protocols, NSJ Bioreagents ensures that Keratin 1 Antibody products deliver accuracy and confidence in both research and diagnostics.
The KRT1 Antibody supports wide-ranging applications in skin biology, pathology, and translational studies.
KRT1 Antibodies identify suprabasal keratinocytes in differentiated epidermis.
The KRT1 Antibody clarifies barrier formation and keratinocyte stratification.
Keratin 1 Antibody reagents support developmental studies of epidermal differentiation.
Mutations in KRT1 cause epidermolytic ichthyosis, making KRT1 Antibodies critical for research.
The KRT1 Antibody detects keratin defects in patient samples and model systems.
Keratin 1 Antibody reagents support mechanistic studies of inherited keratinopathies.
KRT1 Antibodies are used in skin biopsies to distinguish suprabasal keratin expression.
The KRT1 Antibody contributes to diagnosis of palmoplantar keratoderma and ichthyosis.
Keratin 1 Antibody tools support biomarker discovery in inflammatory skin disease.
KRT1 Antibodies detect altered expression in squamous cell carcinoma.
The KRT1 Antibody supports tumor classification and biomarker discovery.
Keratin 1 Antibody reagents are applied in research on keratin remodeling in cancer.
KRT1 Antibodies clarify keratinocyte responses to chronic skin inflammation.
The KRT1 Antibody is used to investigate epithelial stress in psoriasis and dermatitis.
KRT1 Antibodies validate suprabasal keratinocyte identity in engineered skin models.
The KRT1 Antibody ensures accurate epidermal differentiation in stem cell research.
KRT1 Antibodies support therapeutic testing for keratinization disorders.
The KRT1 Antibody is applied in preclinical studies of keratin-targeted therapies.
Keratin 1 Antibody reagents validate biomarkers in dermatology clinical trials.
Keratin 1 is a suprabasal epidermal marker critical for skin resilience, disease, and cancer biology. The KRT1 Antibody provides precise detection of this keratin, while Keratin 1 Antibody reagents more broadly support dermatology, oncology, and regenerative research.
In basic science, KRT1 Antibodies clarify epidermal maturation and cytoskeletal stability. In genetics, the KRT1 Antibody highlights disease-causing mutations in keratinopathies. In oncology, Keratin 1 Antibody tools support cancer classification and therapy development.
Clinically, KRT1 remains an important biomarker for diagnosing inherited skin disorders and stratifying epithelial cancers. By connecting molecular insights with pathology and translational medicine, the KRT1 Antibody continues to support progress in dermatology and oncology.
Keratin 1 is a hallmark of suprabasal epidermis, essential for skin integrity and disease research. The KRT1 Antibody equips scientists and clinicians with a trusted tool for detecting keratin 1, while Keratin 1 Antibody reagents more broadly support discoveries in dermatology, regenerative medicine, and oncology. By bridging molecular research with clinical application, these antibodies remain indispensable for advancing biomedical science and improving patient outcomes.
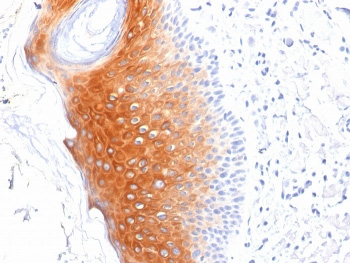
IHC staining of FFPE human skin tissue with KRT1 antibody (clone LHK1).