- Tel: 858.663.9055
 Email: info@nsjbio.com
Email: info@nsjbio.com
- Tel: 858.663.9055
- Email: info@nsjbio.com
AQP1 Antibody reagents target aquaporin 1, a classical water channel and the first aquaporin discovered. AQP1 is expressed broadly across tissues, including kidney, red blood cells, vascular endothelia, and the choroid plexus. Its primary function is to facilitate rapid water transport across membranes, maintaining osmotic balance and fluid regulation.
While kidney physiology remains a core focus, AQP1’s broader significance lies in vascular biology, CSF secretion, and cancer biology. Endothelial AQP1 contributes to angiogenesis, vascular permeability, and fluid dynamics, while choroid plexus expression links it directly to CSF formation and intracranial pressure regulation. Dysregulated AQP1 expression has been implicated in pulmonary hypertension, glaucoma, and tumor growth, making the AQP1 Antibody an essential reagent for diverse biomedical fields. The Aquaporin 1 Antibody further expands applications across translational research and diagnostics.
NSJ Bioreagents provides AQP1 Antibodies validated for immunohistochemistry, western blotting, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and ELISA. Each AQP1 Antibody undergoes rigorous validation for specificity, reproducibility, and assay performance.
By choosing AQP1 Antibodies from NSJ Bioreagents, researchers gain reagents optimized for clarity and consistency. Our antibodies reliably detect AQP1 in endothelial cells, red blood cells, and brain tissue, ensuring reproducible results in both basic research and translational pipelines. Comprehensive datasheets, suggested controls, and optimized protocols support experimental reproducibility across laboratories.
The AQP1 Antibody supports broad applications across vascular biology, CSF regulation, and cancer research.
AQP1 Antibodies detect endothelial expression in capillaries and venules.
The AQP1 Antibody supports studies of vascular permeability and angiogenesis.
Aquaporin 1 Antibody reagents validate biomarkers for vascular remodeling.
AQP1 Antibodies reveal expression in choroid plexus epithelium.
The AQP1 Antibody supports studies of CSF secretion and intracranial pressure.
Aquaporin 1 Antibody reagents extend into research on hydrocephalus and glaucoma.
AQP1 Antibodies detect expression in erythrocyte membranes.
The AQP1 Antibody supports studies of hydration, gas transport, and osmotic regulation.
Aquaporin 1 Antibody reagents provide markers for hematology.
AQP1 Antibodies highlight altered expression in pulmonary hypertension.
The AQP1 Antibody supports research into lung fluid dynamics.
Aquaporin 1 Antibody reagents extend to respiratory disease studies.
AQP1 Antibodies detect dysregulation in tumor angiogenesis.
The AQP1 Antibody supports research into metastasis and tumor survival.
Aquaporin 1 Antibody reagents validate oncology biomarkers.
AQP1 Antibodies are integrated into biomarker-driven vascular and oncology pipelines.
The AQP1 Antibody supports diagnostics for CSF and vascular disorders.
Aquaporin 1 Antibody reagents ensure reproducibility across translational workflows.
AQP1 is a versatile aquaporin with roles spanning vascular biology, CSF secretion, and oncology. The AQP1 Antibody provides validated tools for studying water transport and angiogenesis, while the Aquaporin 1 Antibody expands applications into translational research.
In vascular studies, AQP1 Antibodies highlight its role in angiogenesis and permeability. In neurology, the AQP1 Antibody clarifies mechanisms of CSF production and intracranial regulation. In oncology, Aquaporin 1 Antibody reagents support studies of tumor growth and vascularization.
Clinically, AQP1 is a biomarker for pulmonary hypertension, hydrocephalus, and tumor progression. Reliable AQP1 Antibodies ensure reproducibility and accuracy, bridging discoveries from basic biology to translational and diagnostic applications.
AQP1 is a foundational aquaporin with central roles in vascular biology, CSF regulation, and cancer. The AQP1 Antibody provides validated reagents for angiogenesis, intracranial fluid dynamics, and oncology research, while the Aquaporin 1 Antibody expands these applications into translational pipelines. By ensuring specificity, reproducibility, and assay versatility, these antibodies remain indispensable for advancing vascular biology, brain research, and oncology.
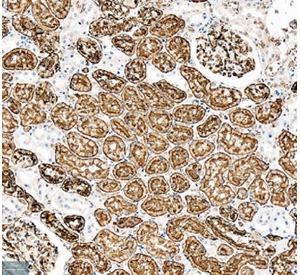
IHC staining of FFPE human kidney tissue with Aquaporin 1 / AQP1 antibody (Cat # R32050). HIER: boil tissue sections in pH8 EDTA for 20 min and allow to cool before testing.