- Tel: 858.663.9055
 Email: info@nsjbio.com
Email: info@nsjbio.com
- Tel: 858.663.9055
- Email: info@nsjbio.com
Cell Biology Antibodies form a versatile toolkit for exploring the molecular networks that underlie cellular structure, function, and communication. Cell biology seeks to understand how proteins, organelles, and signaling pathways coordinate to maintain homeostasis, drive differentiation, and respond to environmental changes. Antibodies directed against key cellular proteins allow researchers to visualize subcellular localization, monitor dynamic processes, and track biomarkers across normal physiology and disease.
These antibodies cover a wide spectrum of targets, including cytoskeletal proteins, nuclear regulators, signaling molecules, ion channels, adhesion molecules, and organelle-specific markers. Because of this breadth, Cell Biology Antibodies support research across immunology, neuroscience, oncology, developmental biology, and translational medicine.
NSJ Bioreagents provides a comprehensive range of Cell Biology Antibodies validated for immunohistochemistry, western blotting, immunofluorescence, ELISA, and flow cytometry. Each antibody undergoes rigorous validation to ensure specificity, reproducibility, and compatibility with common research workflows.
By selecting Cell Biology Antibodies from NSJ Bioreagents, researchers gain reagents optimized for clarity and consistency. Our antibodies deliver robust staining in tissues and cultured cells, reproducible protein detection in lysates, and dependable performance across multiple platforms. Detailed datasheets, validated protocols, and recommended controls further ensure reproducibility in both discovery and clinical research.
The Cell Biology Antibodies collection supports diverse applications across scientific and clinical fields.
Cell Biology Antibodies detect actin, tubulin, keratins, and intermediate filaments.
They clarify cytoskeletal remodeling during migration, division, and adhesion.
Antibodies provide tools to track mechanical responses to stress.
Cell Biology Antibodies highlight mitochondria, lysosomes, endosomes, and nuclei.
They support subcellular localization studies in physiology and pathology.
Antibodies clarify trafficking pathways and organelle biogenesis.
Cell Biology Antibodies detect kinases, phosphatases, and adaptor proteins.
They support mapping of growth factor, immune, and stress pathways.
Antibodies help dissect molecular mechanisms in health and disease.
Cell Biology Antibodies identify dysregulated proteins in cancer.
They support biomarker discovery and therapeutic monitoring.
Antibodies validate oncogenic signaling cascades.
Cell Biology Antibodies track markers of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
They support profiling of immune activation and suppression.
Antibodies contribute to translational immunology and clinical diagnostics.
Cell Biology Antibodies detect neuron- and glia-specific proteins.
They support studies of synaptic proteins and neurotransmission.
Antibodies clarify developmental trajectories in nervous system biology.
Cell Biology Antibodies are validated in biomarker-driven clinical studies.
They provide reproducibility for patient stratification and diagnostics.
Antibodies link basic cellular biology with therapeutic pipelines.
The complexity of cellular systems demands tools that are both specific and versatile. The Cell Biology Antibodies portfolio equips researchers to study everything from structural proteins to signaling regulators.
In basic research, Cell Biology Antibodies enable visualization of organelles, pathways, and structural components. In oncology, they highlight dysregulated networks driving cancer. In immunology, they track immune cell function and signaling. In developmental biology, Cell Biology Antibodies validate lineage markers and differentiation pathways.
Clinically, these antibodies provide biomarkers for diagnostics, guide therapy decisions, and support translational pipelines from bench to bedside. Their reproducibility ensures that laboratory discoveries translate reliably into medical applications.
Cell biology underlies all aspects of life science and medicine, and antibodies are the key tools for revealing its complexity. The Cell Biology Antibodies collection provides validated reagents for studying organelles, pathways, and biomarkers across diverse systems. By ensuring specificity, reproducibility, and broad application, these antibodies remain indispensable for advancing discovery science and clinical research.
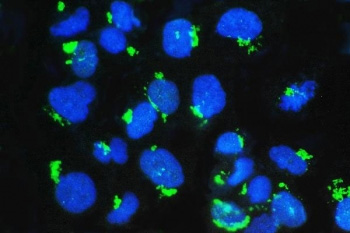
Immunofluorescent staining of FFPE human U-2 OS cells with GM130 antibody (green) and DAPI nuclear stain (blue).