- Tel: 858.663.9055
 Email: info@nsjbio.com
Email: info@nsjbio.com
- Tel: 858.663.9055
- Email: info@nsjbio.com
AQP8 Antibody reagents target aquaporin 8, a unique water channel that contributes to both classical fluid transport and organelle-specific physiology. Unlike some aquaporins with restricted expression, AQP8 is present in multiple tissues, including liver, kidney, testis, colon, and pancreas. Importantly, AQP8 is localized to mitochondria in several cell types, where it helps regulate water balance and hydrogen peroxide transport. This dual role makes AQP8 central to metabolism, oxidative stress regulation, and apoptosis.
In the liver, AQP8 is expressed in hepatocytes and cholangiocytes, where it contributes to bile formation and ammonia handling. In the kidney, it supports fluid absorption in renal tubules. In reproductive tissues, it is involved in sperm maturation and fertility. Because of these diverse roles, the AQP8 Antibody is an indispensable tool for studying metabolism, mitochondrial biology, and systemic physiology. The Aquaporin 8 Antibody complements this by providing assay versatility across experimental systems.
NSJ Bioreagents provides AQP8 Antibodies validated for immunohistochemistry, western blotting, immunofluorescence, ELISA, and flow cytometry. Each AQP8 Antibody is tested for specificity, reproducibility, and cross-platform performance.
By choosing AQP8 Antibodies from NSJ Bioreagents, researchers gain reagents optimized for clarity and consistency. Our antibodies deliver strong staining in hepatic, renal, and mitochondrial preparations, reproducible results in protein lysates, and robust performance across translational studies. Detailed datasheets, suggested controls, and optimized protocols ensure reproducibility across research pipelines.
The AQP8 Antibody supports diverse applications in mitochondrial biology, liver research, reproductive physiology, and translational medicine.
AQP8 Antibodies detect hepatocyte and cholangiocyte expression.
The AQP8 Antibody supports studies of bile secretion and ammonia detoxification.
Aquaporin 8 Antibody reagents provide biomarkers for hepatology research.
AQP8 Antibodies highlight expression in renal tubules.
The AQP8 Antibody supports studies of water absorption and acid–base balance.
Aquaporin 8 Antibody reagents extend applications into nephrology.
AQP8 Antibodies detect mitochondrial localization in multiple tissues.
The AQP8 Antibody supports studies of hydrogen peroxide transport and ROS signaling.
Aquaporin 8 Antibody reagents provide tools for apoptosis and autophagy research.
AQP8 Antibodies detect expression in testis and sperm.
The AQP8 Antibody supports studies of fertility and reproductive physiology.
Aquaporin 8 Antibody reagents clarify water and solute regulation in gametes.
AQP8 Antibodies detect expression in intestinal epithelia and pancreas.
The AQP8 Antibody supports studies of nutrient absorption and digestive physiology.
Aquaporin 8 Antibody reagents extend research into gut and pancreatic disease.
AQP8 Antibodies are applied in biomarker-driven hepatic and mitochondrial studies.
The AQP8 Antibody supports diagnostics for liver and kidney disease.
Aquaporin 8 Antibody reagents ensure reproducibility across translational pipelines.
AQP8 is an aquaporin with unique mitochondrial localization and roles in systemic physiology. The AQP8 Antibody equips researchers with validated tools for studying fluid transport, oxidative stress, and organ-specific functions, while the Aquaporin 8 Antibody expands these applications into translational research.
In liver biology, AQP8 Antibodies highlight hepatocyte and bile duct function. In renal research, the AQP8 Antibody supports studies of water absorption and acid–base regulation. In mitochondrial biology, Aquaporin 8 Antibody reagents provide tools for oxidative stress and apoptosis studies.
Clinically, AQP8 is emerging as a biomarker for liver disease, infertility, and oxidative stress–related disorders. Reliable AQP8 Antibodies ensure reproducibility, linking basic discoveries to diagnostic and therapeutic outcomes.
AQP8 bridges classical aquaporin function with organelle biology. The AQP8 Antibody provides validated reagents for mitochondrial, hepatic, renal, and reproductive studies, while the Aquaporin 8 Antibody expands applications into translational pipelines. By ensuring specificity, reproducibility, and assay versatility, these antibodies remain indispensable for advancing research in fluid transport, metabolism, and oxidative stress.
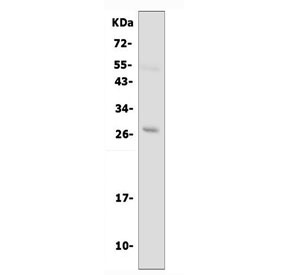
Western blot testing of AQP8 antibody (cat # R30584) and human PC-3 cell lysate. The predicted ~27 kDa protein may be visualized at higher molecular weights due to glycosylation.